How We Provide Fast Web Hosting
To provide quick web hosting, we start by selecting cutting-edge server hardware.
Then we install industry-leading server software (CloudLinux, Imunify 360, and cPanel, MariaDB, LiteSpeed, etc) and set generous limits on configuration settings.
After that, we restrict how many hosting accounts are allowed per server, to ensure resources are never over-committed.
Finally, each server is then put into a maintenance program to routinely monitor performance, network and security and make improvements as necessary.
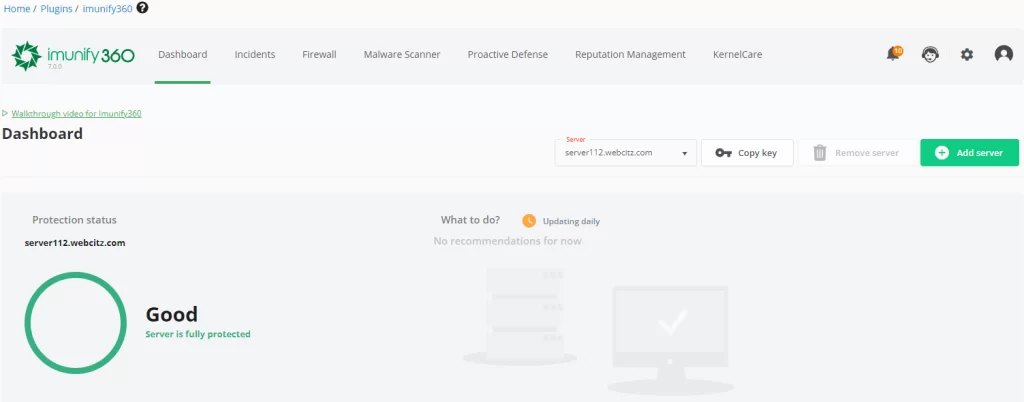
This simple approach to web hosting has allowed us to scale considerably over the years, while maintaining high customer satisfaction and the fastest possible cPanel servers on the market!
Not convinced? No problem! We offer a money back guarantee on your web hosting payment if you are unsatisfied with our web hosting services! Do your digital marketing campaign a favor and switch to a faster web hosting service!
A Few of Our Web Hosting Experts






Pricing for Web Hosting
Listed below you will find the starting price for our performance and high-performance shared web hosting services. The hosting cost increases as more storage space is required.
If you require a domain name, we offer registration and renewal of most domain name extensions for $15.95/year. We also recommend Google Domains, GoDaddy, and NameCheap as third-party domain registrars.
Web Hosting
- 10 GB RAID NVMe Storage
- 100 GB Bandwidth
- 99.9% Network Uptime
- Daily / Weekly Backups
- 4 CPUs, 4GB Memory
High-Performance Web Hosting
- 10 GB RAID NVMe Storage
- 100 GB Bandwidth
- 99.9% Network Uptime
- Daily / Weekly Backups
- 12 CPUs, 12GB Memory
Web Hosting Services for CMS Applications
All of our web hosting services are well-suited for a variety of CMS platforms and PHP frameworks.
The most demanding platforms we host are often Magento installations, but we most often host WordPress websites.
If your website runs on a LAMP-stack, meaning Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP, you’ll be happy with our web hosting.
1.) Fast WordPress Hosting
WordPress is by far the most popular CMS platform on the internet used in web design projects, with more than 40% of all websites on the internet running WordPress.
As you can imagine, we’ve had to put considerable effort into testing the best configurations to provide the fastest web hosting for business websites running WordPress.
For our WordPress hosting services, we recommend installing the LiteSpeed Cache plugin which pairs with the LiteSpeed Web Server software running on the server.
Together, these two systems within our hosting solutions are often enough to help a website pass Google’s Core Web Vitals.
Learn more about our web hosting for WordPress sites.
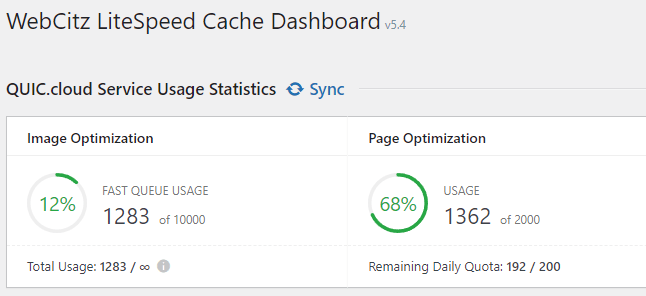
2.) Fast WooCommerce Web Hosting
All of our web hosting services are tuned for WooCommerce ecommerce websites and include access to LiteSpeed caching. This will help ensure your ecommerce development project has fast page load speeds!
3.) Fast Magento 2.x Hosting
All of our web hosting services are tuned for Magento 2 and include LiteMage caching.
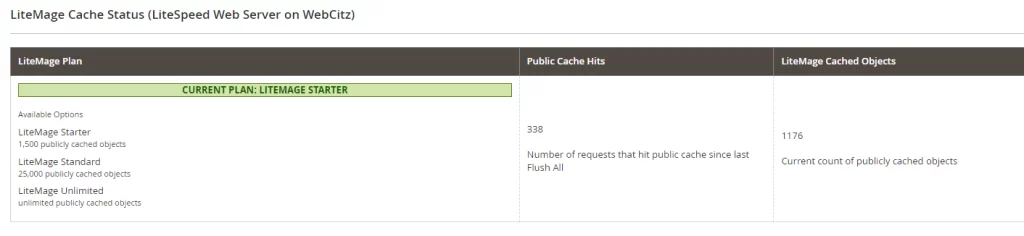
4.) Fast Magento 1.x Hosting
We continue to support Magento 1.x websites on our shared web hosting servers. However, we recommend all Magento 1.x EOL clients purchase a subscription to a third-party web application firewall (WAF) and malware scanning service.
The most popular option we commend is Sucuri, which offers both a WAF and malware scanning service. Another option is Cloudflare Pro, which includes a customizable web application firewall.
Web Hosting FAQs
What is a web hosting service?
In essence, web hosting is an arrangement between you and a web hosting service provider in which you rent and operate a portion of their dedicated servers. These are the computers that will house and process all of your data, as well as allow others to view the content you have so carefully created. Think of it as a storage unit with windows that other Internet users can peer through as they navigate the internet.
You must have a web hosting account in order to operate a website, since no website can simply exist on the Internet without a web server. The only exception would be a website powered by a SaaS solution such as Wix, SquareSpace, or Shopify, since they provide the hosting for you. Most web servers cost thousands of dollars to purchase, not including the costs to house them in a data center, optimize and secure their software applications, and backup the contents on a routine schedule. For this reason, it is more cost-effective to simply lease web hosting from a web hosting provider than attempt to be your own hosting provider.
What is shared hosting?
Shared hosting services are among the most popular types of web hosting due to their affordability and ease-of-use. An individual plan holder has access to a small portion of a web server that is shared by hundreds of other websites. These powerful web servers are divided into “partitions” that are made available to web hosting customers. With a shared web hosting plan, you have access to a set amount of server resources. In the event that you exceed these limitations, resources will be throttled to ensure everyone else on the server is able to continue to operate free of interruption.
A shared hosting plan is a much simpler form of web hosting for the end-user, in comparison to cloud hosting, VPS and dedicated services. That is because the administration of the server environment is done by the web hosting provider instead of the end-user, or a subcontracted 3rd party. Most small businesses gain their first experience with web hosting by purchasing and using a shared web hosting plan, until their resource usage requires a migration to a more powerful hosting service.
What is reseller hosting?
The basic principle is straightforward: you purchase bulk web hosting services and receive a substantial discount. Then you can resell these services for an even greater profit.
A reseller hosting plan is intended to provide you with the tools and resources necessary to run your own web hosting business. A reseller plan holder will have access to a large amount of server resources that can be controlled and delegated by them to their clients. You have control over various configuration settings in order to tailor your hosting plans to your own business model, and you can even brand the control panel to your company. The plans can even be configured and named to suit your specific requirements.
Consider a reseller hosting plan if you are interested in running your own web hosting business.
What is VPS hosting?
Let us first define what VPS stands for – a virtual private server. Simply put, a server is a powerful computer that stores all of the data and files that make up your website. When someone types your domain name into their web browser, that powerful computer displays your website to the searcher.
On to the virtual aspect: VPS utilizes virtualization technology in order to split that one powerful server that we just discussed into multiple virtual servers. Think of it this way: it is one piece of physical hardware that functions as several separate servers. Private means exactly what it implies. The virtual server is dedicated to you, so you will not need to share RAM, CPU, or any resources with other users.
What is dedicated hosting?
Dedicated web hosting means your business or organization has complete control over one or more servers. These servers can be web servers, database servers, load balancers, or any other type of server. In general, dedicated hosting has a high monthly cost in comparison to shared web hosting and VPS hosting services. The main reason for this is you are paying a fixed amount of money for a large, fixed amount of hosting resources. An alternative to this approach would be cloud hosting, where you pay only for the server resources you require in the given moment.
What is disk space?
Disk space refers to the amount of storage allocated to your website. It is very important to have enough disk space because it directly affects the total size limitations of your website(s). If you plan on continuously updating your website(s) with new content, then you will likely require additional disk space in the future.
Suppose, for example, you have 20GB of disk space allocated to your web hosting plan. The total size of the files and databases that make up your website cannot exceed this amount. If you were to exceed the limit, your website may encounter errors or even cease to operate properly.
The amount of disk space is often displayed on all hosting plan sales pages. Please understand any company offering unlimited storage space isn’t truly offering unlimited storage. There will obviously be a limit to the generosity provided by “unlimited storage,” whether that be in the types of files that can be uploaded, the use of the storage space, or simply the total amount deemed reasonable. The amount of disk space available on your web server directly affects how much data can be stored at any given time.
What is bandwidth?
In web hosting, bandwidth is the amount of data that is transferred through your web server over a given period of time.
It is very important to make sure that your website has adequate bandwidth, as this will determine how visitors experience your site, particularly when there is high traffic. Each time a visitor views a page on your website, they consume bandwidth because they are downloading and uploading information. Therefore, a large amount of bandwidth is required to accommodate high traffic levels on a daily basis. This is the primary reason why bandwidth is one of the most important factors to consider when choosing a web hosting plan.
Special Offers for Non-Profits
If the website you need hosted is for a non-profit, check out our non-profit web hosting services to see if you qualify for a free or heavily discounted hosting account!
Hear what our customers are saying












